Weibold Academy: EU-wide end-of-waste criteria for ELT-derived rubber
Weibold Academy article series discusses periodically the practical developments and scientific research findings in the end-of-life tire (ELT) recycling and pyrolysis industry.
This article is a review by Claus Lamer – the senior pyrolysis consultant at Weibold. One of the goals of this review is to give entrepreneurs in this industry, project initiators, investors and the public, a better insight into a rapidly growing circular economy. At the same time, this article series should also be a stimulus for discussion.
ELT derived rubber is ready for EU-wide EoW criteria
Currently rubber recycled from end-of-life tires (ELTs) was ranked 3rd among the most suitable candidate streams for which to develop further EU-wide end-of-waste (EoW) criteria in the European Commission JRC’s report. The European Tyre and Rubber Manufacturers’ association (ETRMA) and the European Recycling Industries’ Confederation (EuRIC) are pleased about this prioritization exercise, although they are right to wonder why there is no date on the horizon.
The 3rd place (after Plastic and Textiles) is still worth a medal, nevertheless. Considering the enormous potential of chemical recycling (pyrolysis) of ELTs, the (very) few missing points could have been made up (author's opinion) and a time horizon might be foreseeable.
Thanks to the efforts of the tyre value chain during the last 25 years, the logistical issue of the collection of End-of-Life Tires (ELT) has been solved through the set-up of ELT Extended Producer Responsibility schemes. And thanks to that, the valuable materials contained in tires have become available for recycling. All tires are collected and treated resulting in a current 95% treatment rate across Europe. Out of the approx. 3 million tonnes of tires reaching end-of-life stage, 1.6 million tonnes are recycled into rubber, steel, and textile fibres. Nevertheless, still more than 1 million tonnes of End-of-Life tires are used in co-incineration in the cement industry.
With one tire going to co-incineration per one tire mechanically recycled into rubber granulate, there is room for improvement in terms of the waste hierarchy. And plenty of untapped potential regarding ELT recycling to help the EU meet the overarching objectives set in The European Green Deal to speed up the transition towards a circular economy and achieve climate neutrality by 2050. (ETRMA & EuRIC Joint Position Paper)
Status under waste management regulation
Management of waste is covered by the Waste Framework Directive (WFD) and related regulations where, inter alia, the main principles for the classification of waste are prescribed. The WFD specifies the conditions when waste ceases to be waste in Article 6 where it outlines four general end-of-waste criteria:
- the use of a substance/object for a specific purpose;
- the existence of market demand for a substance/object;
- compliance of a substance/object with relevant legislation, technical requirements or standards applicable for the products;
- absence of adverse impact on human health and the environment due to the use of a substance/object.
Finally, the WFD delegates the task of determining the end-of-waste status to the EU Member States while mentioning that the EU wide end-of-waste criteria could be developed where relevant. Even the European Commission (2018) noted that currently, it is not clear what measures are taken in the Member States to ensure that the recycled materials meet the end-of-waste criteria and whether they are sufficient and effective.
Different regulatory end-of-waste regimes across the EU may therefore lead to difficulties in introducing the recycled materials on the EU market, and to safety concerns due to various interpretations of the end-of-waste in the Member States. Obviously only an EU-wide end-of-waste regulation, where rules for ceasing to be waste are applicable in all Member States, can have a positive impact on the EU internal market.
With the prioritization by the JRC, the first step towards an EU-wide EoW criteria catalogue for ELT derived rubber was taken, an announcement or recommendation as to when implementation will start as a second step is missing.
10 national EoW criteria for ELT rubber in Europe
There are already 10 national end-of-waste (EoW) criteria for ELTs and ELT-derived rubber in Europe (including United Kingdom) in place. Another 4 states are in preparation. This means that around 50% of the member states had to or will issue national criteria due to the lack of an EU-wide regulation. Without going into the similarities and/or differences here, misunderstandings and/or hurdles in EU internal market seem to be inevitable.
- National end-of-waste criteria in Estonia and France.
- National end-of-waste criteria in Portugal and the United Kingdom for recycled tyres.
- National end-of-waste criteria in the Czech Republic, Denmark, Italy, Portugal, Slovakia, and the United Kingdom for granulates derived from end-of-life tyres, and in the Netherlands for granulates used in infill applications.
- National end-of-waste criteria in preparation in Greece, Spain, Estonia, and Latvia.
Scoping possible further EU-wide end-of-waste criteria for ELTs
The current study was carried out by the Joint Research Centre and the Directorate-General for the Environment and aimed to support the Commission in the implementation of both the Circular Economy Action Plan and the Waste Framework Directive by:
- identifying a list of priority waste or by-product streams for which to develop further EU-wide end-of-waste or by-product criteria (scoping); and
- deriving a shortlist of top-candidate streams for which to develop further EU-wide end-of-waste or by-product criteria.
The potential of candidate streams was appraised using 12 ranking criteria:
- level of support from stakeholders to develop further EU-wide end-of-waste or by-product criteria;
- current collection and material re-use/recycling rates;
- identified uses, types of uses (recycling versus other recovery operations) and impacted economic sectors;
- estimated EU market value;
- intra-EU shipments;
- extra-EU shipments;
- purity/composition of recovered materials;
- possibility to recover critical raw materials;
- evidence of demand;
- existence of relevant international or national product standards;
- existence of national or regional end-of-waste or by-product criteria; and
- expected environmental and human health impacts.
The overall potential took into consideration the scores obtained for each ranking criterion (three level scoring or traffic light) and the relative importance given to each criterion for the objectives of this study.
Based on the methodology developed for this purpose, and the data and information provided by stakeholders, the candidate streams were ranked based on their overall potential for the further development of EU-wide end-of-waste or by-product criteria. The streams with a higher overall potential (top tercile) were identified as priority streams (objective 1).
The identified priority list includes the following waste/by-product categories and streams in the top tercile:
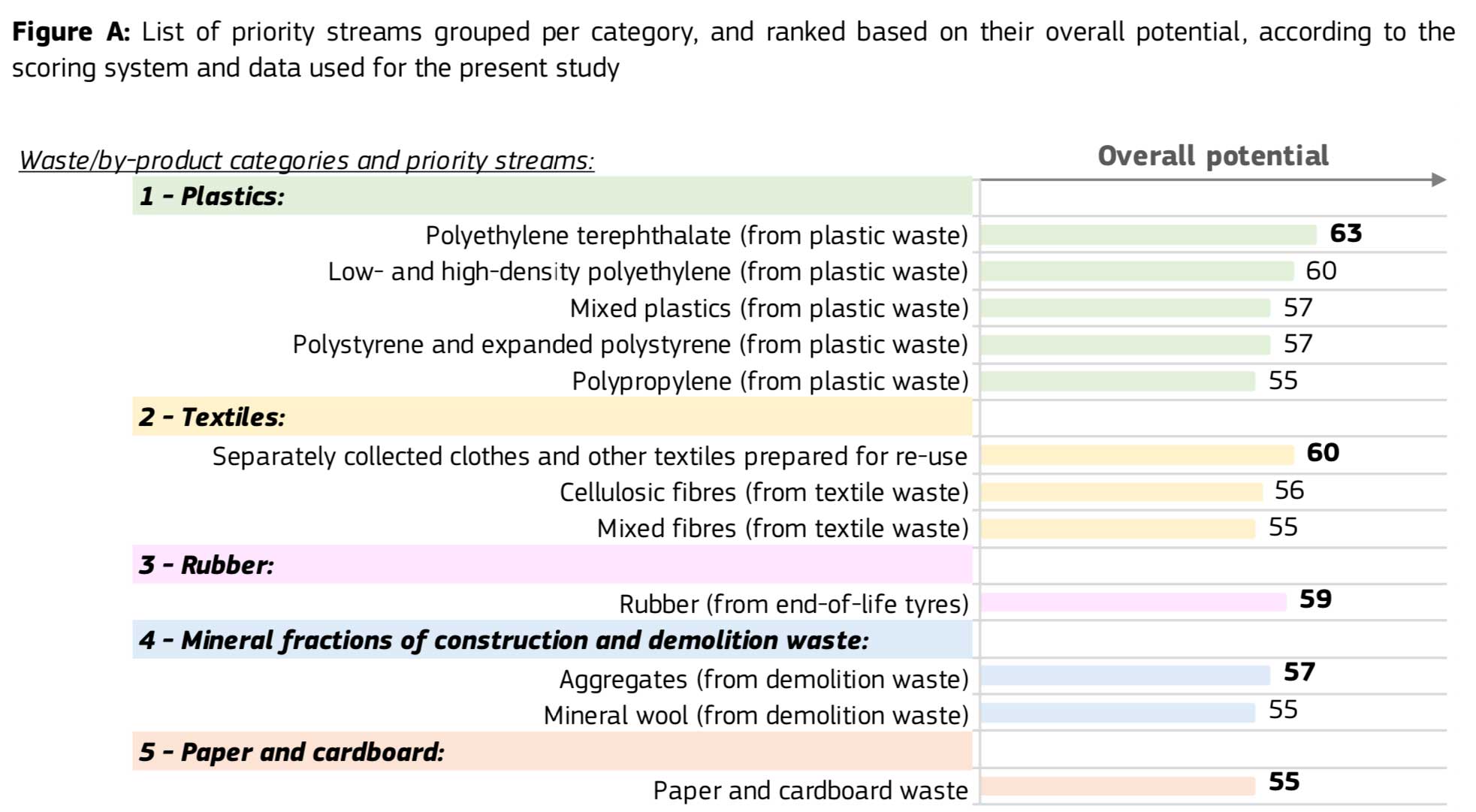
Source: European Commission JRC’s report (March, 2022).
JRC’s ranking of ELT-derived rubber
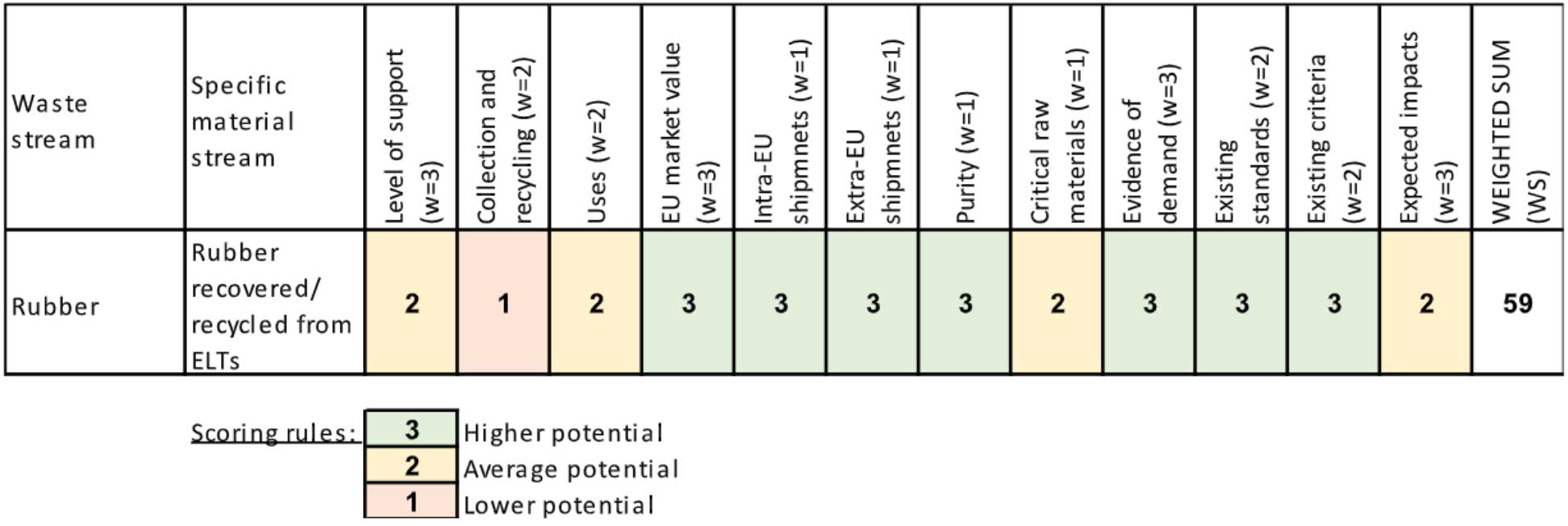
Source: European Commission JRC’s report (March, 2022), Weibold (June, 2022).
Reasons given by JRC for the rating (selected points commented):
Level of support (average potential): Supported by industry representatives but opposed by environmental NGOs representatives and reported as not a priority stream by one or more Member States’ representatives.
Collection and recycling (lower potential): ELT material recycling rated with 50-60%. Collection rated at ~90%. Candidate material streams for which higher material re-use/recycling rates (50-60%) and higher collection rates (~90%) were reported, were considered as having a lower potential to increase their re-use/recycling rate, and therefore a lower potential for EU-wide end-of-waste or by-product criteria and were given a score of 1 (red).
Author's note: As still more than 1 million tonnes of ELTs are going to co-incineration in cement kilns per year, there is a high potential for improvement in terms of the waste hierarchy, e.g., through chemical recycling (pyrolysis) to valuable and sustainable secondary raw materials, such as recovered carbon black and pyrolysis oils! Therefore, a significantly higher score of 3 (green) should be given.
Uses (average potential): An average lower impact on the economy based on the number of impacted economic sectors and uses promoting recycling over other recovery operations was seen and therefor (only) a score of 2 (yellow) was given.
Author's note: The enormous potential for improvement in terms of the waste hierarchy of chemical recycling was "overlooked" in this criterion! Interestingly, the chemical industry (plastic production, carbon black) was explicitly mentioned as potential. Therefore, a higher potential for EU-wide end-of-waste or by-product criteria and a score of 3 (green) should be given.
Critical raw materials (average potential): The objective of this criterion was to differentiate between candidate streams for which recovery of critical raw materials is possible, which would then be considered as having a higher potential for the development of further EU-wide criteria. More importance was given to streams for which recovery of critical raw materials is possible as one of the objectives of developing further EU-wide end-of-waste or by-product criteria is to prevent critical raw materials losses.
Author's note: Even if the possibility of recovering critical raw materials by stakeholders (average potential) was affirmed, a higher rating would be justified if the high potential for substitution of fossil-based raw materials through the chemical recycling (pyrolysis) of ELTs were taken into account.
Expected impacts (average potential): The objective of this criterion was to differentiate between candidate streams with potentially higher benefits and lower risks for the environment and human health, which would then be considered as having a higher potential for the development of further EU-wide criteria. Material streams from ELTs were considered as having (only) an average potential for EU-wide end-of-waste or by-product criteria and were given a score of 2 (yellow).
Author's note: Although the positive environmental effects were acknowledged in principle, unjustified risks were cited, which reduces the high potential to an average level.
Conclusion
Rubber recycled from end-of-life tires (ELTs) was currently ranked 3rd among the most suitable candidate streams for which to develop further EU-wide end-of-waste (EoW) criteria. The European Tyre and Rubber Manufacturers and the European Recycling Industries are pleased about this prioritization, although they are right to wonder why a timeline horizon was not established.
From the point of view of the chemical recycling industry (ELT pyrolysis), its enormously high potential for helping the EU to meet the overarching objectives set in The European Green Deal to speed up the transition towards a circular economy and achieve climate neutrality by 2050 was insufficiently (almost not at all) considered. If this potential were given due consideration, rubber and recovered environmentally sustainable chemical feedstocks deriving from ELTs would be a top-priority candidate (and not "just" third-place finisher).
Literature: Orveillon G., Pierri E., Egle L., Gerbendahl A., Wessman P., Garcia John E. and Saveyn H. G. M., Scoping possible further EU-wide end-of-waste and by-product criteria, EUR 31007 EN, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, 2022, ISBN 978-92-76-49046-3, doi:10.2760/067213, JRC128647. The reuse of this document is authorised under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) licence (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Weibold is an international consulting company specializing exclusively in end-of-life tire recycling and pyrolysis. Since 1999, we have helped companies grow and build profitable businesses.









