Weibold Academy: Research progress: Innovative new applications for rCB
Weibold Academy article series discusses periodically the practical developments and scientific research findings in the end-of-life tire (ELT) recycling and pyrolysis industry.
These articles are reviews by Claus Lamer – the senior pyrolysis consultant at Weibold. One of the goals of the review is to give entrepreneurs in this industry, project initiators, investors and the public, a better insight into a rapidly growing circular economy. At the same time, this article series should also be a stimulus for discussion.
For the sake of completeness, we would like to emphasize that these articles are no legal advice from Weibold or the author. For legally binding statements, please refer to the responsible authorities and specialist lawyers.
Introduction
In a world grappling with environmental challenges, finding ways to recycle and repurpose materials has never been more critical. At the heart of this movement is recovered carbon black (rCB), an innovative material derived from end-of-life tires (ELTs) through pyrolysis. This promising material offers a pathway to sustainable, high-value applications that can help reshape industries ranging from energy to environmental remediation.
At the Smithers Recovered Carbon Black Asia Conference held on September 24-25, 2024, the spotlight was on the latest research and breakthroughs in the field, particularly through a scientific collaboration between Weibold Consulting and Green Avengers R&D Solutions. Their work presented by Yogesh Gaikwad, Weibold’s expert for carbon blacks, showcased how rCB can play a vital role in producing next-generation materials with wide-ranging benefits for both the economy and the environment.
A New Horizon for rCB Applications
Traditional uses of recovered carbon black (rCB) primarily focus on lower-value applications like rubber and plastics. However, recent breakthroughs have unlocked the potential for rCB to substitute ultra-high-value products, such as photosensitive carbon quantum dots (CQDs) and magnetic graphene oxide (MGO).
Substituting Photosensitive Carbon Quantum Dots (CQDs) with rCB
Carbon Quantum Dots are nanoscale particles that possess unique fluorescence and photosensitivity properties. These particles, typically less than 10 nanometers in size, can be synthesized through various methods such as laser ablation, pyrolysis, and electrochemical oxidation. Using rCB as a precursor, rCB-based CQDs can reduce waste and promote a circular economy while producing a cost-effective, high-performance material.
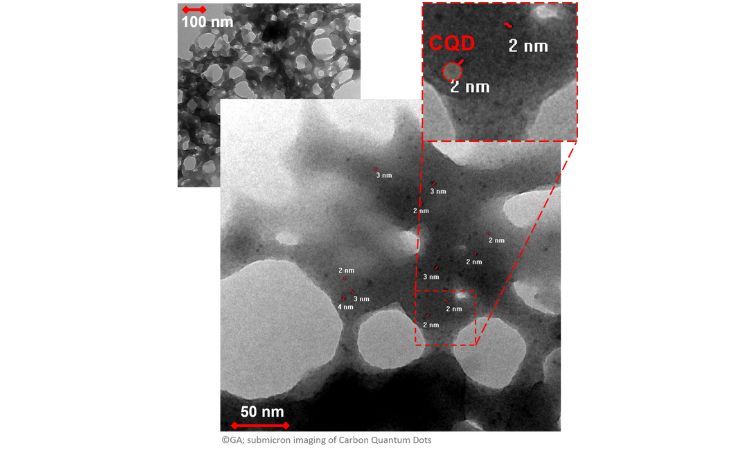
RCB-based CQDs (see submicron imaging of rCB-based CQDs) are particularly suited for energy conversion applications, including solar cells, LEDs, and photocatalysis for hydrogen production. They also have promising uses in environmental remediation, such as the degradation of pollutants and the detection of heavy metal ions. Beyond energy and the environment, rCB-based CQDs show potential in advanced sectors like optoelectronics and bioimaging, where their strong fluorescence and biocompatibility make them excellent candidates for medical applications, such as drug delivery and cellular imaging.
Substituting Magnetic Graphene Oxide (MGO) with rCB
Magnetic graphene oxide is another groundbreaking material that could transform the water purification industry. By substituting traditional graphite with rCB, Weibold Consulting, and Green Avengers R&D Solutions have created magnetic rCB (m-rCB), combining the adsorptive properties of activated carbon with magnetic functionality (see photo). This allows for easy separation of contaminants from water using external magnetic fields, an advantage over conventional filtration methods that often require energy-intensive processes.
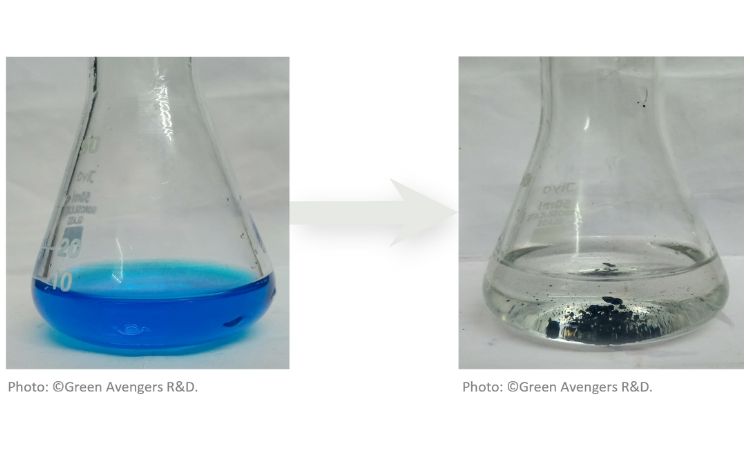

The benefits of m-rCB extend beyond water treatment. This material has shown promise in catalysis, particularly for reducing organic pollutants and supporting the catalytic degradation of hazardous compounds. Its versatility, coupled with its cost-effectiveness, positions magnetic rCB as a strong competitor in sustainable industrial processes.
The Circular Economy in Action
What makes these innovations particularly compelling is their alignment with circular economy principles. Recovered carbon black not only reduces waste but also serves as a valuable input for high-tech industries. This reduces the need for raw materials, cuts down on energy consumption, and helps minimize the environmental footprint of production processes.
As Weibold Consulting and Green Avengers R&D demonstrate, using rCB for advanced applications offers substantial economic benefits. For instance, magnetic graphene oxide produced from rCB can be tailored to specific industries, such as chemical sensing, water purification, or energy storage. The high market prices for these specialized materials of up to 3 million USD per metric ton for specialized products like magnetic graphene oxide underscore the financial incentive for companies to invest in rCB-based solutions.
Sustainable Materials of the Future
The potential for recovered carbon black to revolutionize industries hinges on the ability to scale these innovations. Weibold Consulting, in collaboration with Green Avengers R&D, has committed to developing commercially viable production methods for these high-value materials. With ongoing research into the synthesis of CQDs and m-rCB, the stage is set for rCB to move from niche scientific discovery to mainstream industrial application.
Moreover, the environmental benefits of rCB-based materials cannot be overstated. As global industries seek ways to reduce their carbon footprint, materials like CQDs and m-rCB offer energy-efficient, reusable, and versatile alternatives to traditional solutions. The ability of m-rCB to perform consistently across multiple cycles without significant loss in performance adds a layer of economic sustainability, making it a long-term solution for industries seeking greener practices.
Conclusion
As the world faces the dual challenge of managing waste and finding sustainable alternatives to finite resources, recovered carbon black emerges as a beacon of innovation. Through collaborations such as those seen between Weibold Consulting and Green Avengers R&D Solutions, the future of rCB looks bright, with wide-ranging applications that promise both ecological and economic rewards.
The work showcased at the Recovered Carbon Black Asia Conference underscores the importance of investing in sustainable technologies that support circular economies. As the recovery of Carbon Black (rCB) continues to evolve, it could soon play a pivotal role in industries ranging from energy to medicine, offering an environmentally responsible path forward for global production.
Source:
Weibold Presentation at Smithers rCB Conference in Qingdao, PR China, September 2024
Weibold is an international consulting company specializing exclusively in end-of-life tire recycling and pyrolysis. Since 1999, we have helped companies grow and build profitable businesses.









